How to prepare an OPE file for Hyper Suprime-Cam
Last update: June 19, 2025
Index
1. What is an OPE file?
2. Structure of an OPE file
3. Detailed description of PARAMETER_LIST section
3.1. Object list
3.2. Non-sidereal tracking
4. Detailed description of Command section
4.1. Calibration frames
4.1.1. Bias, Dark
4.1.2. Dome flat
4.1.2.1. On-axis dome flat
4.1.2.2. Normal dome flat
4.1.3. Standard stars
4.2. Main exposures
4.2.1. Single-shot mode
4.2.2. Five-shot mode with dithering
4.2.3. N-shot mode with dithering
4.3. Other operations
4.3.1. Focusing
4.3.2. Filter exchange
5. Requirements and Recommendations
6. Other useful information
• Grammatical tips for OPE files
• Overheads regarding various actions
• Tools and tips
• OPE file Editor (hoe)
1. What is an OPE file?
Observations of Subaru Telescope are conducted by executing script files called 'OPE file (Observation Procedure Execute file; but often called OPEration file)'. Observers are requested to prepare the OPE file describing the sequence of your observing tasks prior to your run. An OPE file consists of information on your targets and individual operating commands such as target acquisition, exposing, focusing, filter change, etc. Please prepare for your OPE files and send them to the Support Astronomer (SA) by e-mail. On the observing night, SA and telescope operator will load your OPE file onto the observation control system and perform the observation by following your requests.
Each individual command will be executed by SA and telescope operator on a line-by-line basis. Since operators can choose any command line to execute in your OPE file and you may also edit and modify the OPE file at the summit, command lines do not have to be sorted exactly in the order of your observation plan. However, if you write down command lines in a sorted order with reasonable comment, it would be helpful for SA to understand your intent correctly and to prevent misoperation.
You may include all the targets in one OPE file. However, it would be a good idea to separate your OPE file into reasonably small files especially by each night in the case you awarded two or more nights and have a lot of targets with multiple filters/modes to observe.
Template OPE file
The template OPE file can be downloaded from here.
Please follow this template file and the description below to prepare your OPE file.
2. Structure of an OPE file
An OPE file is composed of three parts. All parts should be included in the OPE file.
-
HEADER
-
Described between <HEADER> and </HEADER>
-
Information on the file name and observing date and time
-
The information listed here does not have to be the exact amount.
-
-
PARAMETER_LIST
-
Described between <PARAMETER_LIST> and </PARAMETER_LIST>
-
Several preset parameters (e.g., $DEF_TOOLS) are defined here. Please do not modify or remove them.
-
Your target list and parameters which can be referred to in the COMMAND part (see below) are defined here.
-
You can also define object names (written into fits header), coordinates, position angle of your target fields.
-
-
COMMAND
-
Described between <COMMAND> and </COMMAND>
-
Commands for operating the instrument and the telescope are listed here.
-
One line contains one command.
-
3. Detailed description of PARAMETER_LIST section
3.1. Object list
Example:
NGC77145=OBJECT="NGC7714/7715" RA=233618.320 DEC=+020921.28 EQUINOX=2000.0
L1551=OBJECT="L1551" RA=043130.000 DEC=+181000.00 EQUINOX=2000.0
NGC6822=OBJECT="NGC6822" RA=+194456.000 DEC=-144806.00 EQUINOX=2000.0
NGC4038_39=OBJECT="NGC4038_39" RA=120201.250 DEC=-184554.00 EQUINOX=2000.0
NGC4826=OBJECT="NGC4826" RA=125644.100 DEC=+214634.94 EQUINOX=2000.0
M20=OBJECT="M20" RA=180222.100 DEC=-225548.00 EQUINOX=2000.0
M51=OBJECT="M51" RA=132955.000 DEC=+471855.00 EQUINOX=2000.0
SA107=OBJECT="SA107" RA=153904.500 DEC=-001400.00 EQUINOX=2000.0
Parameters:
-
***=OBJECT="###": Definition of the object name. "***" will be the alias name used in the OPE file. "###" will be written in the fits header.
-
RA: Right ascension of the object ("hhddss.sss")
-
DEC: Declination of the object ("±ddmmss.ss")
-
EQUINOX: Equinox of the coordinates
Description:
-
This command is used to define the object to observe.
-
Accepted format for "RA" and "DEC" are "hhddss.sss" and "±ddmmss.ss", respectively. Do not use "hh:mm:ss", "hh mm ss", etc. Both must have three or fewer decimal places.
-
Alphabets, numeric characters, and "_" (underscore) are only accepted in the "***" part of "OBJECT" parameter. Do not use "+", "−", etc.
3.2. Non-sidereal tracking
Example:
NEO1=OBJECT="NEO 1" FILE="08 20001231neo1.eph"
Parameters:
-
***=OBJECT="###": Definition of the object name. "***" will be the alias name used in the OPE file. "###" will be written in the fits header.
-
FILE: File with non-sidereal tracking information
Description:
-
This command is used to define the object to observe with non-sidereal tracking.
-
An additional eph file which describes pointing coordinates is needed. See information here before creating eph files. It is recommended to use JPL HORIZONS System to prepare eph files for solar system objects. Do not erase "08" in the "FILE" parameter.
-
Alphabets, numeric characters, and "_" (underscore) are only accepted in the "***" part of "OBJECT" parameter. Do not use "+", "−", etc.
4. Detailed description of COMMAND section
4.1. Calibration frames
4.1.1. Bias, Dark — GetBias, GetDark —
Example:
GetBias $DEF_IMAGE NUMBER=10
GetDark $DEF_IMAGE EXPTIME=300 NUMBER=5
Parameters:
-
GetBias
- NUMBER: Number of frames to be taken
-
GetDark
-
NUMBER: Number of frames to be taken
-
EXPTIME: Exposure time (2–1200 sec in integer; usually 300 sec)
-
Description:
-
These commands are used to take bias or dark frames.
-
Since HSC has small gaps in the dome shutter causing light leaks from the outside, you should take these calibration data when the outside is dark enough in the case you need accurate bias and dark frames for reduction. It is accepted to take these frames from 30 min after sunset to 30 min before sunrise.
-
Usually, five dark frames with 300-sec exposures and 10 bias frames are taken every HSC observation run. Because all calibration data will be shared through the observers in the same run (see here), you may not have to obtain your own bias and dark frames.
4.1.2. Dome flat
4.1.2.1. On-axis dome flat — SetupOnAxisDomeflat / GetDomeFlat — [ updated on Mar 23, 2023 ]
Example:
SetupOnAxisDomeFlat $DEF_TOOLS Z=3.75 INSROT_POS=90
GetDomeFlat $DEF_IMAGE EXPTIME=8 Filter="HSC-r2"
GetDomeFlat $DEF_IMAGE EXPTIME=8 Filter="HSC-r2" NUMBER=9
Parameters:
-
SetupOnAxisDomeFlat
-
Z: Focus position. Please use "3.75".
-
INSROT_POS: Rotator angle. Please use "90".
-
-
GetDomeFlat
-
EXPTIME: Exposure time (sec)
-
NUMBER: Number of flat frames to be taken
-
Note:
Other parameters included in the example are just used for confirmation.
It is recommended to use these parameters, but note that they will not change the status of the telescope or HSC.
Description:
-
HSC dome flats have been fully shifted (except for some user filters) from the normal ones with flat lamps on the telescope top ring to those with a single lamp (so-called "on-axis lamp") attached on the top of HSC camera unit as the default science calibration data since the S21A February run.
-
Dome flats for the general broad-band filters (i.e., g, r2, i2, z, and Y) should be obtained with the on-axis lamp, while those for NB/IB/EB filters should be obtained with the normal flat lamps on the telescope top ring.
-
"SetupOnAxisDomeFlat" configures the instrument and the telescope for the dome flat. "GetDomeFlat" command takes dome flat frames.
-
To make sure the count in the flat frame is appropriate, "GetDomeFlat" command is usually divided into two parts; the counts of the first flat frame will be checked before taking the rest of the flat frames.
-
Typical exposure times to obtain flat frames with the peak count of around 18000 ADU may be found in the latest template OPE file.
-
Obtaining dome flats are accepted from 30 min after sunset to 30 min before sunrise.
-
To ensure the stability of the flat lamp brightness, flat frames are able to be obtained 10 min after turning on the lamps.
-
Due to the time limitation, only one sort of flat frame can be taken before or after observation (e.g., take HSC-r2 flats in the evening, and then take HSC-i2 flats in the morning).
-
Because all the calibration data (including flats) will be shared through the observers in the same run, you may not have to obtain flat frames if they were taken in the previous observations. Conversely, if you are the one who is using a certain filter for the first time in the run, you generally have to take the flat frames during the evening twilight.
-
4.1.2.2. Normal dome flat — SetupDomeflat / GetDomeFlat — [ updated on Mar 23, 2023 ]
Example:
SetupDomeFlat $DEF_TOOLS SETUP=SETUP Z=3.75 INSROT_POS=0 LAMP=4X600W VOLT=100.0 AMP=5.10
GetDomeFlat $DEF_IMAGE EXPTIME=11 Filter="NB0400"
GetDomeFlat $DEF_IMAGE EXPTIME=11 Filter="NB0400" NUMBER=9
ShutdownDomeFlat $DEF_CMNTOOL
Parameters:
Detailed information of parameters with "*" are described in the description below.
-
SetupDomeFlat
-
SETUP: Setup mode*
-
Z: Focus position. Please use "3.75".
-
INSROT_POS: Rotator angle. Please use "0".
-
LAMP: Flat lamp used for Dome flat*
-
VOLT: Voltage of the flat lamp*
-
AMP: Electric current of the flat lamp*
-
GetDomeFlat
-
EXPTIME: Exposure time (sec)
-
NUMBER: Number of flat frames to be taken
-
-
ShutdownDomeFlat
- ShutdownDomeFlat has no parameter to set.
Note:
Other parameters included in the example are just used for confirmation.
It is recommended to use these parameters, but note that they will not change the status of the telescope or HSC.
Description:
-
Dome flats for NB/IB/EB filters should be obtained with the normal flat lamps on the telescope top ring.
-
"SetupDomeFlat" configures the instrument and the telescope for domeflats, including dome lamp settings, position angle, etc. GetDomeFlat command takes dome flats. "ShutdownDomeFlat" turns off the lamps.
-
"SETUP=SETUP" parameter will power cycle the dome lamps and change the voltage and electric current to the requested value. Meanwhile, "SETUP=CHANGE" parameter will just change the voltage and electric current (it will not turn on the lamp).
-
Dome Flat Configurations:
Typical combinations of appropriate dome lamp settings and exposure times may be found in the latest template OPE file.
These configurations are set to obtain flat frames with the peak count of 18000 ADU.-
Obtaining dome flats are accepted from 30 min after sunset to 30 min before sunrise.
-
To ensure the stability of the flat lamp brightness, flat frames are able to be obtained 10 min after turning on the lamps.
-
Due to the time limitation, only one sort of flat frame can be taken before or after observation (e.g., take HSC-r2 flat in the evening, and then take HSC-i2 flat in the morning).
-
Because all the calibration data (including flats) will be shared through the observers in the same run, you may not have to obtain flat frames if they were taken in the previous observations. Conversely, if you are the one who is using a certain filter for the first time in the run, you generally have to take the flat frames during the evening twilight.
-
4.1.3. Standard Stars — SetupField / GetStandard —
Example:
SetupField $DEF_IMAGE $SA107 OFFSET_RA=40 OFFSET_DEC=90 FILTER="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=-90
GetStandard $DEF_IMAGE $SA107 EXPTIME=5 DELTA_Z=0.4 OFFSET_RA=40 OFFSET_DEC=90 FILTER="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=-90
Parameters:
-
SetupField
-
OFFSET_RA: Offset to be added to RA of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
-
OFFSET_DEC: Offset to be added to DEC of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
-
INSROT_PA: Position angle (deg)
-
-
GetStandard
-
EXPTIME: Exposure time (10 sec or more in integer)
-
DELTA_Z: Offset of the telescope focus
-
Note:
• Please use "OFFSET_RA"=40, "OFFSET_DEC"=90, and "INSROT_PA"=-90 to ease the operation,
in the case you do not have any particular value.
• Other parameters included in the example are just used for confirmation.
It is recommended to use these parameters, but note that they will not change the status of the telescope or HSC.
Description:
-
These commands are used to take a standard star field.
-
"SetupField" moves the telescope to point the specified coordinates with a specified position angle ("INSROT_PA"). "OFFSET_RA" and "OFFSET_DEC" are the offsets to be added to the RA and Dec of the target field, respectively (See here for information of CCD arrangement and position angle).
-
Since usual spectrophotometric standards are single objects, "OFFSET_RA", "OFFSET_DEC", and "INSROT_PA" are used to prevent the star placing in the gap of the CCD.
-
"GetStandard" command changes the telescope focus by "DELTA_Z" (= defocusing) and then makes one exposure at the position where the telescope is pointing. After the exposure is done, the telescope focus will be set back to the original position.
-
Note that "GetStandard" command never changes the telescope pointing and the position angle by "OFFSET_RA", "OFFSET_DEC" and "INSROT_PA" parameters. They are only for confirmation and the consistency with other commands. In the case you want to execute standard star observations with several settings (i.e., different offsets, different PAs, etc.), you should use the "SetupField" command first.
-
Defocusing:
In general, popular standard stars (such as Landolt's stars or typical spectrophotometric stars) are generally too bright for on-focus imaging with HSC to obtain reasonable photon counts in the linearity range even with a shortest exposure time. Therefore, defocusing is usually needed for standard star observations. Typically, reasonable defocusing on the order of 0.2–0.4 mm is needed for exposing 12–13 mag stars for "EXPTIME" = 10 sec using broad band filters. Any stars brighter than 11 mag would be unavailable.
4.2. Main Exposures
4.2.1. Single-shot mode — SetupField / GetObject with $DEF_IMAGE / $DEF_IMAGE_VGW —
Example:
1. with open-tracking
SetupField $DEF_IMAGE $NGC77145 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 FILTER="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
GetObject $DEF_IMAGE $NGC77145 EXPTIME=240 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 FILTER="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
2. with auto-guiding
SetupField $DEF_IMAGE_VGW $NGC6822 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 GOODMAG=14.5 AG_EXP=0.2 AG_AREA=SINGLE SELECT_MODE=SEMIAUTO Filter="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
GetObject $DEF_IMAGE_VGW $NGC6822 EXPTIME=360 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 GOODMAG=14.5 AG_EXP=0.2 AG_AREA=SINGLE SELECT_MODE=SEMIAUTO Filter="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
Parameters:
-
SetupField
-
OFFSET_RA: Offset to be added to RA of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
-
OFFSET_DEC: Offset to be added to DEC of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
-
INSROT_PA: Position angle (-180 – 180 in deg)
Parameters for "with auto-guiding" mode (see description below for details):
-
GOODMAG: Guide star brightness (mag)
-
AG_EXP: Exposure time for guiding (sec)
-
SELECT_MODE: AG mode selection (SEMIAUTO or MANUAL)
-
-
GetObject
- EXPTIME: Exposure time (2–1200 sec in integer)
Note:
Other parameters included in the example are just used for confirmation.
It is recommended to use these parameters, but note that they will not change the status of the telescope or HSC.
Description:
-
These commands are used to take single-shot exposure at a specified field.
-
"SetupField" moves the telescope to point the specified coordinates with a specified position angle ("INSROT_PA"). See here for information of CCD arrangement and position angle).
-
"OFFSET_RA" and "OFFSET_DEC" are the offsets to be added to the RA and Dec of the target field, respectively.
-
"GetObject" command makes one exposure with "EXPTIME" at the position where the telescope is pointing. Exposure time should be 2–1200 sec in integer. Use the HSC Exposure Time Calculator to calculate the appropriate value.
-
Note that "GetObject" command for the single-shot mode never changes the telescope pointing and the position angle by "OFFSET_RA", "OFFSET_DEC" and "INSROT_PA" parameters. They are only for confirmation and the consistency with other commands. In the case you want to execute single-shot observations with several settings (i.e., different offsets, different PAs, etc.), you should use the "SetupField" command first.
-
Auto-guiding:
Four CCDs place in the outer edge of the field-of-view (SDO-ID = 2_01, 2_02, 2_17, and 2_18) are for auto-guiding. This means that the images for auto-guiding are those taken with filters, as same as the science data. A star which is taken with the guiding CCDs will be automatically selected as a guide star based on the GOODMAG value with "SELECT_MODE=SEMIAUTO" mode. In "SELECT_MODE=MANUAL" mode, you can select a guide star interactively with the observing control system. In most case, "SELECT_MODE=SEMIAUTO" with an appropriate value of "GOODMAG" and "AG_EXP" will work.
Appropriate combinations of "GOODMAG" and "AG_EXP" are as follows. Note that customizations of these values are needed to adjust the weather condition.
| Filter | "GOODMAG" | "AG_EXP" |
|---|---|---|
| HSC-g | 13.5 | 0.2 |
| HSC-r2 | 14.5 | 0.2 |
| HSC-i2 | 14.0 | 0.2 |
| HSC-z | 13.0 | 0.3 |
| HSC-Y | 14.0 | 0.3 |
| NB0387 | 11.5 | 10.0 |
| NB0515 | 12.5 | 0.5 |
| NB0816 | 12.5 | 0.5 |
| NB0921 | 12.5 | 0.5 |
| NB0973 | 12.5 | 0.5 |
- Non-sidereal tracking:
Use this single-shot mode with open-tracking for non-sidereal objects.
4.2.2. Five-shot mode with dithering — SetupField / GetObject with $DEF_IMAGE5 / $DEF_IMAGE5_VGW —
Example:
1. with open-tracking
SetupField $DEF_IMAGE5 $L1551 DITH_RA=120 DITH_DEC=120 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 Filter="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
GetObject $DEF_IMAGE5 $L1551 DITH_RA=120 DITH_DEC=120 EXPTIME=240 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 Filter="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
2. with auto-guiding
SetupField $DEF_IMAGE5_VGW $NGC4038_39 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 DITH_RA=120 DITH_DEC=120 GOODMAG=14.5 AG_EXP=0.2 SELECT_MODE=SEMIAUTO Filter="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
GetObject $DEF_IMAGE5_VGW $NGC4038_39 EXPTIME=360 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 DITH_RA=120 DITH_DEC=120 GOODMAG=14.5 AG_EXP=0.2 SELECT_MODE=SEMIAUTO Filter="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
Parameters:
Detailed information of parameters with "*" are described in the description below.
-
SetupField
-
DITH_RA: Dithering parameter for RA direction (arcsec). This parameter should be 60 or more.*
-
DITH_DEC: Dithering parameter for Dec direction (arcsec). This parameter should be 60 or more.*
-
OFFSET_RA: Offset to be added to RA of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
-
OFFSET_DEC: Offset to be added to DEC of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
-
INSROT_PA: Position angle (-180 – 180 in deg)
Parameters for "with auto-guiding" mode (see description "Auto-guiding" in section 4.2.1.)
-
GOODMAG : Guide star brightness (mag)
-
AG_EXP : Exposure time for guiding (sec)
-
SELECT_MODE: AG mode selection (SEMIAUTO or MANUAL)
-
-
GetObject
-
EXPTIME: Exposure time (2–1200 sec in integer)
-
DITH_RA: Dithering parameter for RA direction (arcsec). This parameter should be 60 or more.*
-
DITH_DEC: Dithering parameter for Dec direction (arcsec). This parameter should be 60 or more.*
-
OFFSET_RA: Offset to be added to RA of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
-
OFFSET_DEC: Offset to be added to DEC of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
Note:
1. Other parameters included in the example are just used for confirmation. It is recommended to use these parameters,
but note that they will not change the status of the telescope or HSC.
2. "DITH_RA", "DITH_DEC", "OFFSET_RA", and "OFFSET_DEC" parameters must be same between "SetupField" and "GetObject".
Otherwise, the dithering motion would be made in an unexpected manner. -
Description:
-
These commands are used to take five exposures at a specified field with a predefined five-point dithering pattern.
-
"SetupField" command moves the telescope to point the specified coordinates with a specified position angle ("INSROT_PA") (See here for information of CCD arrangement and position angle).
-
"OFFSET_RA" and "OFFSET_DEC" are the offsets to be added to the RA and Dec of the target field, respectively.
-
"GetObject" command makes five exposures with exposure time = "EXPTIME" with telescope dithering described below. Exposure time should be 2–1200 sec in integer. Use the HSC Exposure Time Clculator to calculate the appropriate value.
-
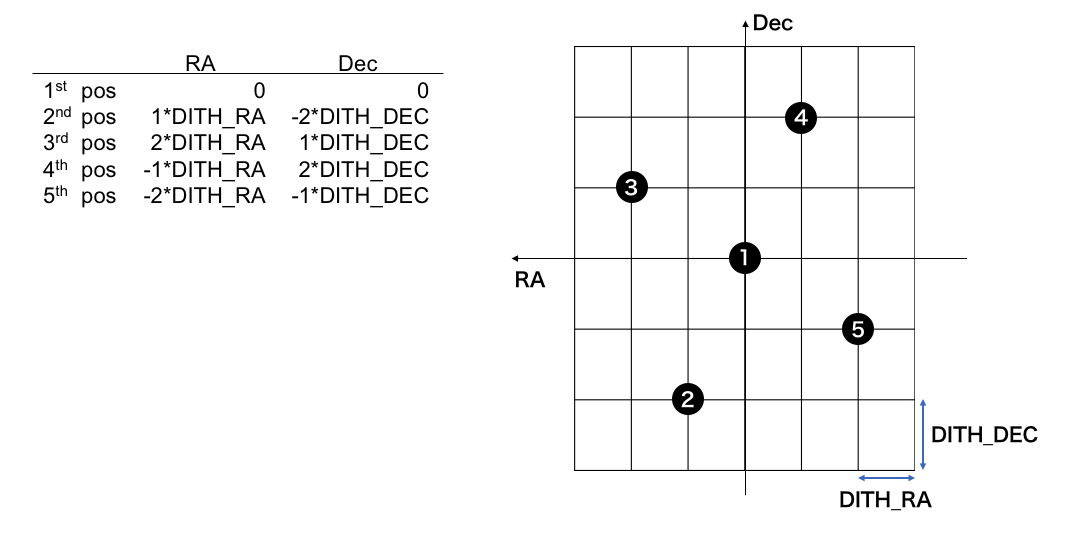
Dithering pattern of Five-shot mode:
Predefined dither pattern of the five-shot mode is as follows (relative to the center (0,0), which is the point given by the object information and the offsets). "DITH_RA" and "DITH_DEC" should be 60 or more.-
If you need to start the exposures from the (i+1)-th position, add SKIP=i to BOTH of "SetupField" and "GetObject".
Example:
Start from 1st shot: "SKIP=0"
Start from 2nd shot: "SKIP=1"
···
Start from 5th shot: "SKIP=4" -
If you need to stop the exposures by the j-th position, add STOP=j to BOTH of "SetupField" and "GetObject".
Example:
End at 1st shot: "STOP=1"
End at 2nd shot: "STOP=2"
···
End at 5th shot: "STOP=5" -
You can combine the "SKIP" and "STOP" parameters. For example, "SKIP=1" and "STOP=4" will take the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th shots of the five-point dithering.
-
4.2.3. N-shot mode with dithering — SetupField / GetObject with $DEF_IMAGEN / $DEF_IMAGEN_VGW —
Example:
1. with open-tracking
SetupField $DEF_IMAGEN $L1551 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 NDITH=3 RDITH=120 TDITH=15 Filter="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
GetObject $DEF_IMAGEN $L1551 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 EXPTIME=240 NDITH=3 RDITH=120 TDITH=15 Filter="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
2. with auto-guiding
SetupField $DEF_IMAGEN_VGW $NGC4038_39 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 NDITH=3 RDITH=120 TDITH=15 GOODMAG=14.5 AG_EXP=0.2 SELECT_MODE=SEMIAUTO Filter="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
GetObject $DEF_IMAGEN_VGW $NGC4038_39 EXPTIME=360 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 NDITH=3 RDITH=120 TDITH=15 GOODMAG=14.5 AG_EXP=0.2 SELECT_MODE=SEMIAUTO Filter="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
Parameters:
Detailed information of parameters with "*" are described in the description below.
-
SetupField
-
NDITH: Number of shots*
-
RDITH: Radius of the circular dithering (arcsec). RDITH should be between 120 and 1620.*
-
TDITH: Offset angle of the starting position (deg)*
-
OFFSET_RA: Offset to be added to RA of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
-
OFFSET_DEC: Offset to be added to DEC of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
-
INSROT_PA: Position angle (-180 – 180 in deg)
Parameters for "with auto-guiding" mode (see description "Auto-guiding" in section 4.2.1.)
-
GOODMAG : Guide star brightness (mag)
-
AG_EXP : Exposure time for guiding (sec)
-
SELECT_MODE: AG mode selection (SEMIAUTO or MANUAL)
-
-
GetObject
-
EXPTIME: Exposure time (2–1200 sec in integer)
-
NDITH: Number of shots*
-
RDITH: Radius of the circular dithering (arcsec). RDITH should be between 120 and 1620.*
-
TDITH: Offset angle of the starting position (deg)*
-
OFFSET_RA: Offset to be added to RA of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
-
OFFSET_DEC: Offset to be added to DEC of the target (-3600 – 3600 in arcsec)
Note:
1. Other parameters included in the example are just used for confirmation. It is recommended to use these parameters,
but note that they will not change the status of the telescope or HSC.
2. "NDITH", "RDITH", "TDITH", "OFFSET_RA", and "OFFSET_DEC" parameters must be same between SetupField and GetObject.
Otherwise, the dithering motion would be made in an unexpected manner. -
Description:
-
These commands are used to take N shots (N="NDITH") at a specified field with an N-point circular dithering pattern.
-
"SetupField" command moves the telescope to point the specified coordinates with a specified position angle ("INSROT_PA") (See here for information of CCD arrangement and position angle).
-
"OFFSET_RA" and "OFFSET_DEC" are the offsets to be added to the RA and Dec of the target field, respectively.
-
"GetObject" command makes "NDITH" time exposures with "EXPTIME" with telescope dithering described below. Exposure time should be 2–1200 sec in integer. Use the HSC Exposure Time Clculator to calculate the appropriate value.
-
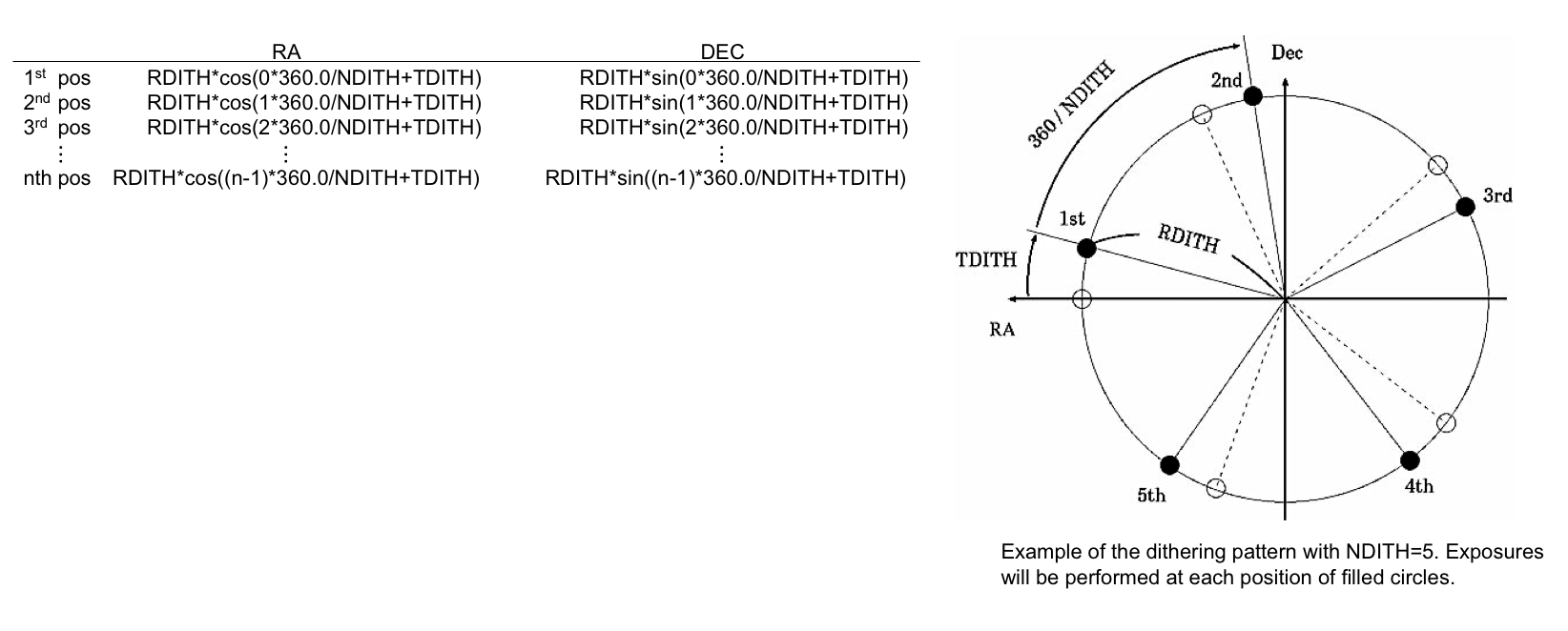
Dithering pattern of N-shot mode:
The dithering pattern of this mode is defined as below. The center of the dithering circle is the point given by the object information and the offsets. The listed positions are the relative values to the center of the dithering circle.-
In the case if you set "NDITH=5", "TDITH=0" and "INSROT_PA=0", the offset of the RA direction between 2nd and 5th
(and also between 3rd and 4th) exposure will be equal (this case is described with open circles in the figure above).
This sort of dithering pattern will drop a certain star into the gap of CCDs for twice or more during the dithering observation,
which may reduce the quality of the data. When you conduct N-shot dithering mode, we encourage you to determine the appropriate value of
"NDITH", "RDITH", "TDITH", and "INSROT_PA". -
It is recommended to use "TDITH=10" for "NDITH"=5 or 8, "TDITH"=5 for "NDITH"=7, and "TDITH"=15 for other "NDITH" values.
Please note that large "NDITH" increases the risk of deviation in the offset angle when the dithering is unexpectedly
interrupted in the middle. -
If you need to start/stop the exposures at i-th position, use the "SKIP" and/or "STOP" parameter in BOTH of "SetupField" and "GetObject" (see description of section 4.2.2).
-
4.3. Other operations
4.3.1. Focusing — FOCUSOBE —
Example:
FOCUSOBE $DEF_IMAGE $NGC77145 EXPTIME=10 Z=3.25 DELTA_Z=0.05 DELTA_DEC=5 Filter="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
Parameters:
-
EXPTIME: Exposure time (usually 10 sec)
-
Z: Central Z-axis position during focusing (mm)
-
DELTA_Z: Shift amount of Z during focusing (mm)
-
DELTA_DEC: Offset in DEC direction during focusing (arcsec)
-
INSROT_PA: Position angle (-180 – 180 in deg)
Note:
Other parameters included in the example are just used for confirmation.
It is recommended to use these parameters, but note that they will not change the status of the telescope or HSC.
Description:
-
This command performs multiple exposures for focusing.
-
This command will first move the telescope to point the provided coordinates.
-
Focusing will be conducted by taking seven frames by changing the Z-axis position of HSC and nodding the telescope toward DEC direction. CCD readout will be conducted after all seven exposures are finished.
-
The optimum value of "Z" is 3.2–3.7. This value will be customized by SA during the observation.
-
By setting "RA=!STATS.RA" and "DEC=!STATS.DEC" parameters, you can perform the focusing at the current telescope position.
-
To conduct focusing with non-sidereal tracking objects, use "SetupField" command before running "FOCUSOBE", as described below.
SetupField $DEF_IMAGE $NEO1 OFFSET_RA=0 OFFSET_DEC=0 FILTER="HSC-r2" INSROT_PA=0
FOCUSOBE $DEF_IMAGE RA=!STATS.RA DEC=!STATS.DEC OBJECT="FOCUS TEST" EXPTIME=10
4.3.2. Filter exchange — FilterChange1, FilterChange2—
Example:
FilterChange1 $DEF_TOOLS FILTER="HSC-r2"
FilterChange2 $DEF_TOOLS FILTER="HSC-r2" MIRROR=CLOSE
Parameters:
- FILTER: Filter to be inserted
Description:
-
These commands conduct the filter exchange of HSC.
-
"FilterChange1" first set the telescope, rotator angle, etc. to the proper position for filter exchange and then changes the filter.
-
"FilterChange2" prepares the telescope and HSC to resume the observation.
-
Aliases for HSC filters are below:
HSC-g, HSC-r2, HSC-i2, HSC-z, HSC-Y,
NB0387, NB0391, NB0395, NB0400, NB0430,
NB0468, NB0497, NB0506, NB0515, NB0527,
NB0656, NB0718, NB0816, NB0872, NB0921,
NB0926, NB0973, NB1010, IB0945, EB-gri
5. Requirements and Recommendations
When we proceed your HSC observation, we would like to ask you some requirements and recommendations listed below, which may take some observation time from you.
Requirements
-
Take 10 or more dome flats in each band at least once per HSC observing run
-
Use the same configuration for each filter (appropriate lamp voltage, current, and instrument rotator angle should be 0)
-
Keep the dome flat lamp on for 10 min before starting exposures for warm up
-
To avoid light leak from outside, dome flats should be taken 30 min after the sunset/before the sunrise
-
-
Take a shot of 30 sec exposure for photometric calibration*
-
Every time after filter change
-
At least three times per night: at the beginning, middle, and end of the night (can be shared with 2-a.)
-
When you take only long exposures (≥ 2 min/shot), take a 30 sec exposure on at least one of the fields according to 2-a. and 2-b.
* As the Pan-STARRS1 catalog is available in HSC pipeline from February 2017, calibration frame does not have to be obtained with the SDSS fields.
-
-
If you take short exposures (≤ 60 sec) continuously more than 20 shots, the on-site analysis system may be stopped by the SA to avoid the stall of the system. You may continue observation but information from the on-site analysis system will not be available. When you restart the long exposure (> 60 sec), on-site analysis system will be restarted.
Recommendations
-
Take five or more bias frames at the beginning and end of each night
-
In small dither, use dither steps of r > ~120 arcsec for the IMAG_N mode, and r > ~60 arcsec for the IMAG5 mode.
-
Continuous short exposures (< 3 sec) more than 20 shots should be strongly discouraged because it would cause a data transfer stall.
6. Other useful information
Grammatical tips for OPE files
-
You cannot divide long commands into several lines.
-
Unpermitted characters
The following expressions are not allowed or should be avoided in OPE file.-
Any quotations in comment lines — e.g., # exposure in i' band, "double quotations"
-
Any semicolons in comment lines — e.g., # B band ; 3x12min
-
-
Upper/lower case
- The commands used in the OPE file are not case-sensitive except the characters within the double quotations.
Overheads regarding various actions
-
Telescope slew
In the azimuthal direction, dome rotation takes 3 min per 90 deg (0.5 deg/sec). -
Observation overhead
approx. 35 sec including wiping, readout, etc. -
Instrument rotator
60 sec for changing the PA by 90 deg. Turning the instrument rotator can be done at the same time with CCD readout. -
Auto-guiding
Auto-guiding works from 30 sec after the exposure starts, and ends 10 sec before the exposure finishes.
Therefore auto-guiding is effective for long exposures (> 60 sec).
It is recommended to use auto-guiding for exposure longer than 240 sec. -
Filter exchange
approx. 30 min (incl. focus check)
Tools and tips
-
Field-of-view of HSC
To check the field-of-view with Aladin, please see HSC FoV Check with Aladin.